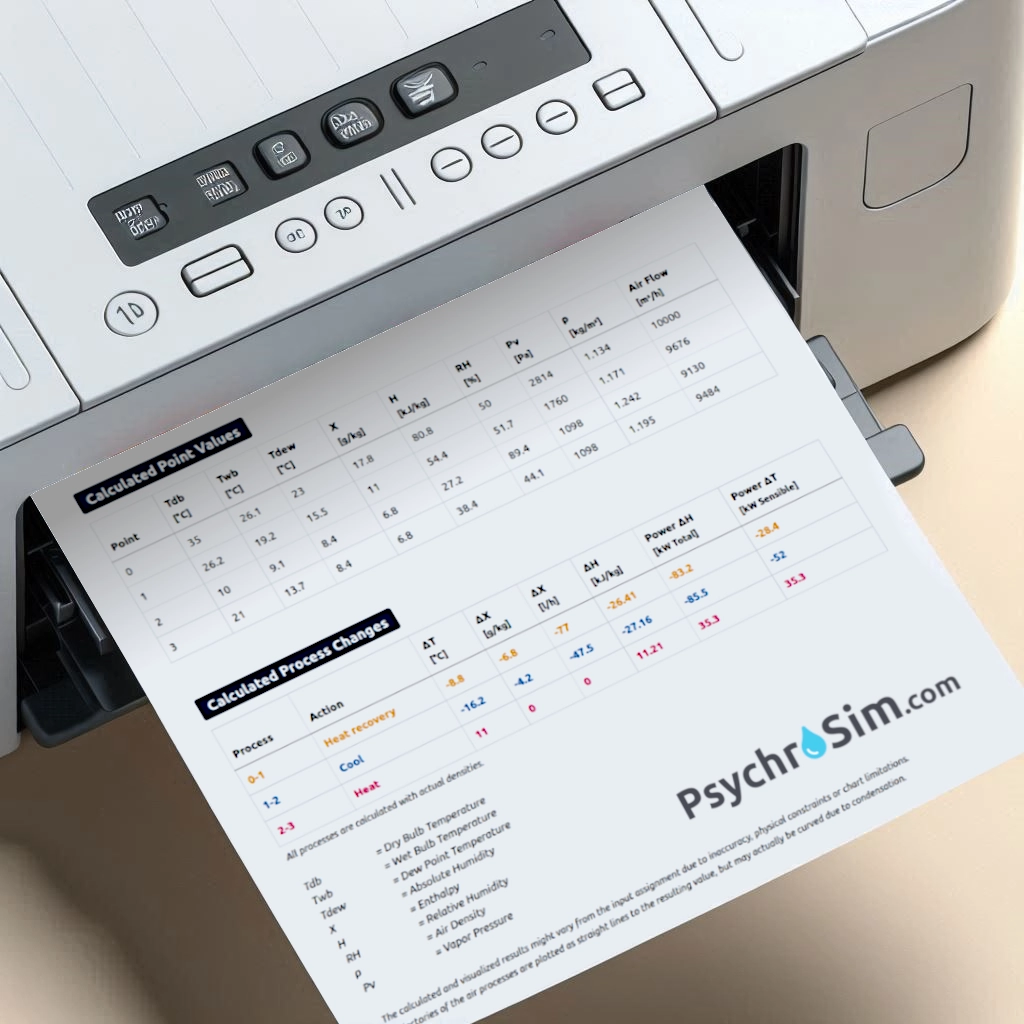
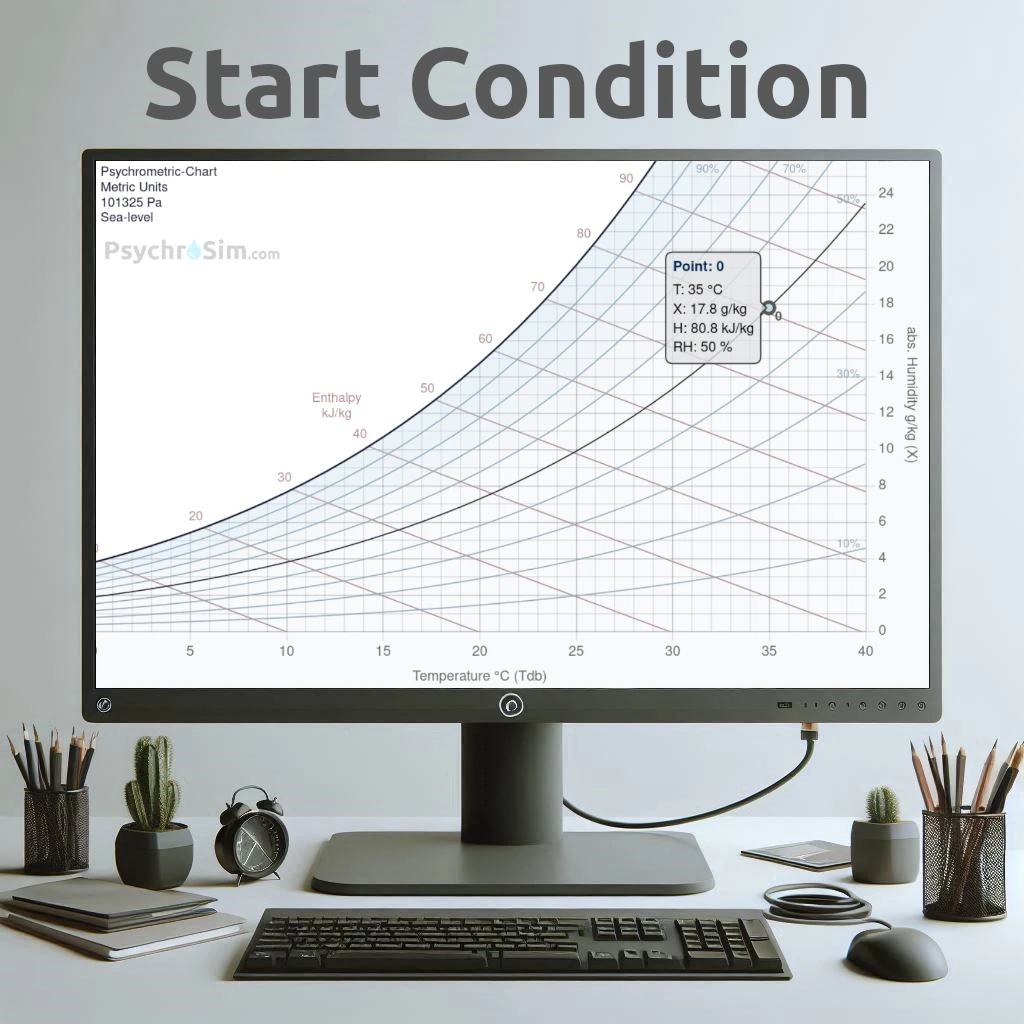
Chart Settings
Upon accessing the tool, you will have the opportunity to set your general settings. Choose your preferred
chart style and
language, and select the
unit system that you are familiar with.
- Chart Style: Mollier/ Psychrometric-Chart. The x/y-axes will be flipped.
- Chart Language: Input and output fields will be translated to your selected language.
- Units-system: Metric(SI) or Imperial(I-P). This affects the chart, input and calculated values.
In the chart settings (icon under the chart), you can adjust the
Temperature Axis and
Humidity Ratio Axis, enable and set your
Comfort Area and define the
Air Density.
- Axes: By adjusting the ranges, you can focus on just a part of the diagram.
- Comfort Area: This is the range of the desired Temperature and Humidity. On/Off or customizable.
- Density is standard set to actual Density (dynamic value). If enabled, the calculator will use the uniform density you set (fixed value).